Virtual Host Server
Certainly! Here’s some information organized under specific headings related to virtual host servers:
Definition:
- Definition:
- Virtual Host Server, also known as virtual hosting or shared hosting, allows multiple websites to be hosted on a single physical server.
- Each website has its own domain name and appears as if it has its own dedicated server, but in reality, it shares server resources with other websites.
- Purpose:
- Virtual host servers are used to maximize resource utilization and cost-effectiveness by hosting multiple websites on a single server.
- They provide an affordable hosting solution for small to medium-sized websites that do not require the full resources of a dedicated server.
- Name-based Virtual Hosting:
- Name-based virtual hosting is the most common method used in virtual host servers.
- The server distinguishes between incoming requests based on the domain name specified in the HTTP headers.
- Multiple websites share the same IP address, and the server routes the requests to the appropriate virtual host based on the domain name.
- IP-based Virtual Hosting:
- IP-based virtual hosting assigns a separate IP address to each virtual host.
- The server uses the IP address of the incoming request to determine which virtual host should handle it.
- This method is typically used when specific requirements cannot be met with name-based virtual hosting, such as SSL certificate restrictions.
Configuration:
- Configuration:
- Virtual host servers require configuration to set up and manage the virtual hosts.
- Configuration involves defining domain names, specifying directories for website files, and configuring access controls and security settings.
- Server configuration files or control panels provided by hosting platforms used for virtual host configuration.
- Document Root:
- Each virtual host has a specific directory known as the document root or web root.
- The document root is the starting point for serving the website’s files and content.
- When a request made to a virtual host, the server looks for the requested file within the document root associated with that virtual host.
.
Virtual host servers offer a scalable and cost-effective solution for hosting multiple websites on a single server, allowing efficient resource utilization and effective website management.
Sure! Here are some detailed explanations of the headings related to virtual host servers:
- Virtual Host Configuration:
- Virtual host configuration involves setting up and managing the virtual hosts on the server.
- It typically includes defining the domain names, specifying the directories where website files stored, configuring access controls, and setting security parameters.
- Virtual host configuration can done through server configuration files or control panels provided by hosting platforms.
- Name-based Virtual Hosting:
- Name-based virtual hosting a method where multiple websites hosted on a single IP address.
- The server uses the “Host” header in the HTTP request to determine which virtual host should handle the request.
- Each virtual host associated with a specific domain name, and the server routes the request to the appropriate virtual host based on the domain name specified in the header.
IP-based Virtual Hosting:
- IP-based Virtual Hosting:
- IP-based virtual hosting assigns a separate IP address to each virtual host.
- The server uses the IP address of the incoming request to determine which virtual host should handle it.
- This method is less common and typically used when specific requirements cannot met with name-based virtual hosting, such as when SSL certificates require a dedicated IP.
- Document Root:
- The document root, also known as the web root, the directory on the server where the website’s files and directories stored.
- Each virtual host has its own document root, which serves as the starting point for serving the website’s content.
- When a request made to a virtual host, the server looks for the requested file within the document root associated with that virtual host.
Virtual servers provide an efficient and flexible way to multiple websites on a single physical server while maintaining separation and security between them.
separation and security between them
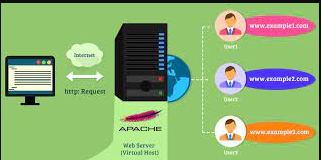
A virtual host , also known as hosting or shared hosting, refers to a method of hosting multiple websites on a single physical . Each website has its own domain name and appears as if it has its own dedicated server, but in reality, it shares resources (such as processing power, memory, and storage) with other websites on the same server.
When setting up a virtual server, you typically configure the server to respond to multiple domain names or hostnames, allowing each website to have its own unique identity. The server distinguishes between the incoming requests based on the domain name specified in the HTTP headers of the request.
Here are some important headings or concepts related to virtual host servers:
- Host Configuration: This refers to the process of setting up and configuring the hosts on the server. It involves specifying the domain names, directories where the website files stored, and other parameters such as security settings and access controls.
- Name-based Hosting: This is the most common type of virtual hosting, where the uses the “Host” header in the HTTP request to determine which host should handle the request. This allows multiple websites to share the same IP address.
- IP-based Hosting: In this method, each virtual assigned a separate IP address. And the uses the IP address of the incoming request to determine which host should handle it. This approach less common and typically used when specific requirements cannot be met with name-based virtual hosting.
- Document Root: Each virtual host has a specific directory on the server known as the document root or web root. This directory contains the website’s files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.). And is the starting point for serving the website’s content.




